Why Do Shielded Cables Matter For Signal Integrity And EMI Control?
Shielded cables play a critical role in maintaining signal integrity in environments where electromagnetic interference is present. As data rates increase and electronic systems become more densely packed, unwanted electrical noise can distort signals, increase error rates, and reduce system reliability. Shielding provides a controlled path for interference to dissipate, allowing electrical and data signals to propagate with predictable performance.
How Electromagnetic Interference Affects Cabling
Electromagnetic interference, commonly referred to as EMI, is generated whenever electrical current flows. Sources include motors, power supplies, radio transmitters, lighting systems, and even adjacent data cables. EMI can couple into signal conductors through radiation or induction, altering voltage levels and timing characteristics.
When interference reaches a certain threshold, it can corrupt data frames, increase retransmissions, or cause intermittent link failures that are difficult to diagnose. These effects are especially problematic in high speed digital systems where signal margins are already narrow.
How Shielding Improves Signal Integrity
Shielding introduces a conductive layer around the insulated conductors that acts as a barrier to external noise. When properly grounded, the shield intercepts electromagnetic energy and redirects it away from the signal path. This reduces both ingress of external interference and egress of noise generated by the cable itself.
By stabilizing the electrical environment around the conductors, shielded cables help preserve waveform shape, timing accuracy, and amplitude consistency. This directly translates to lower bit error rates and more predictable link behavior.
Shielded Versus Unshielded Cable Behavior
Unshielded cables rely primarily on conductor geometry, such as twisted pairs, to reduce susceptibility to noise. While effective in low interference environments, this approach has limitations when exposed to strong or broadband EMI sources.
Shielded cables provide an additional layer of protection that is independent of pair balance. This makes them more resilient in electrically noisy settings and better suited for applications where consistent performance is required regardless of surrounding equipment.
Types of Shielding and Their Impact
Different shielding methods offer varying balances of coverage, durability, and flexibility.
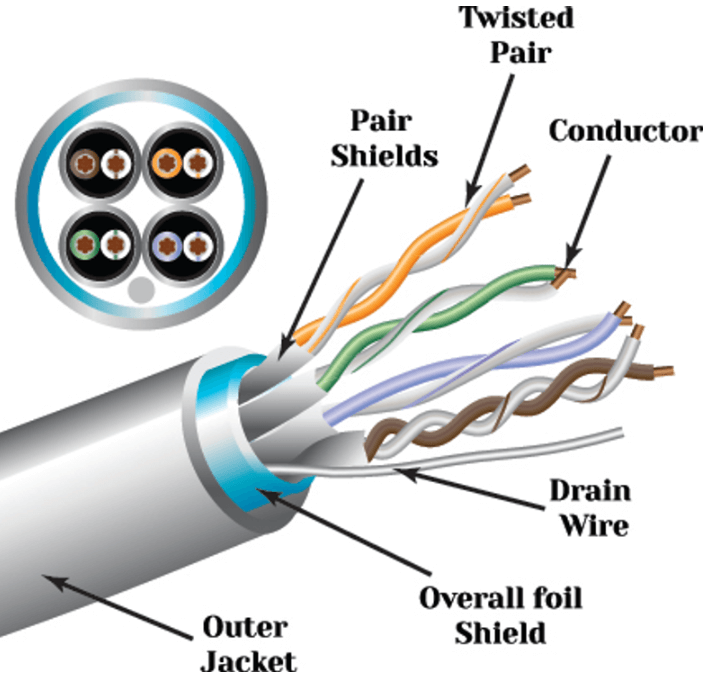
Foil shielding provides nearly complete coverage against high frequency interference but is mechanically fragile and typically requires a drain wire for grounding. It is best suited for fixed installations with minimal movement.
Braided shielding uses woven copper strands to form a durable, low resistance shield. While coverage is slightly lower than foil, braided shields handle mechanical stress better and offer superior grounding performance.
Some cables combine foil and braid to achieve both broad frequency protection and physical robustness. These hybrid designs are common in demanding industrial and data center environments.
Importance of Proper Grounding
Shielding is only effective when it is correctly grounded. An ungrounded or improperly grounded shield can behave like an antenna, worsening interference rather than reducing it. Ground continuity must be maintained through connectors, patch panels, and equipment chassis to ensure noise is safely dissipated.
Grounding practices should align with system design, local electrical codes, and manufacturer guidance to avoid ground loops or safety hazards.
Typical Environments where Shielding is Required
Shielded cables are commonly used in the following scenarios:
-
Industrial automation and control systems
-
Data centers with high port density and power equipment
-
Medical and diagnostic devices
-
Audio and video systems sensitive to noise
-
Military, aerospace, and transportation platforms
In these environments, the cost and complexity of shielding are outweighed by the need for reliability and predictable performance.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Do shielded cables eliminate all electromagnetic interference?
No. Shielding reduces the impact of EMI but does not completely eliminate it. Proper system design and grounding are still required.
Are shielded cables always better than unshielded cables?
Not necessarily. In low noise environments, unshielded cables may perform adequately and offer easier installation.
Does shielding affect cable flexibility?
Yes. Shielded cables are typically thicker and less flexible due to the additional conductive layers.
Can shielded cables be mixed with unshielded cabling?
They can, but grounding and connector compatibility must be carefully managed to avoid performance issues.