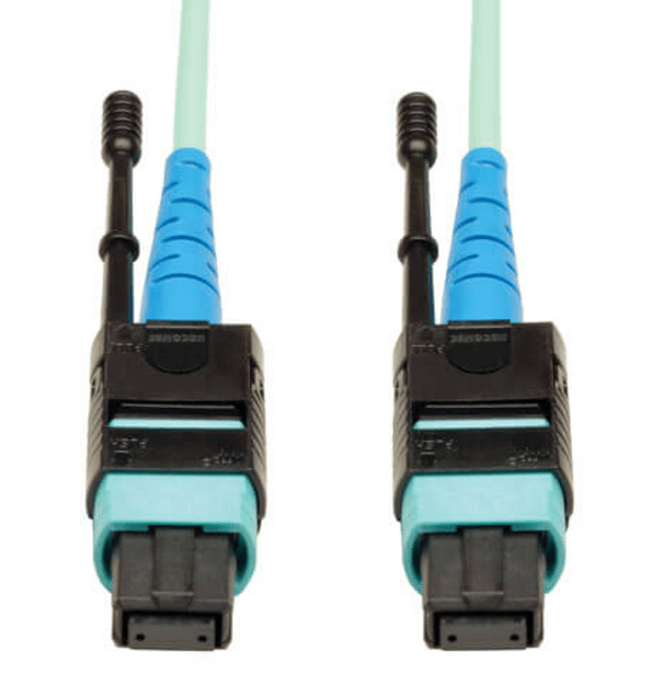
When Should MTP And MPO Cabling Be Used Instead Of Duplex Fiber
As data center bandwidth requirements increase, traditional duplex fiber connections can become a limiting factor in both density and scalability. MTP and MPO cabling provides a multi fiber alternative that consolidates multiple optical channels into a single connector and cable assembly. This approach is preferred in environments where high bandwidth, parallel optics, and structured fiber management are required, particularly in QSFP based links and backbone architectures.
Density And Port Efficiency Considerations
Duplex fiber uses one transmit and one receive fiber per link, which works well for lower speed or sparse deployments. As link speeds increase, especially at 40 Gb and above, relying on multiple duplex connections quickly consumes panel space and cable pathways.
MTP and MPO connectors carry multiple fibers, commonly 8, 12, or more, within a single interface. This allows significantly higher port density at patch panels and switches, making them well suited for high capacity racks and aggregation areas where space efficiency is critical.
Support For Parallel Optical Interfaces
Many high speed transceivers rely on parallel optics rather than serial transmission. QSFP plus and similar interfaces use multiple optical lanes operating simultaneously to achieve aggregate bandwidth.
MTP and MPO cabling aligns multiple fibers in a single connector, allowing each lane to be mapped directly from transceiver to transceiver. Duplex fiber cannot support this architecture without multiple discrete connections, which increases complexity and risk of misrouting.
Backbone And Trunk Cabling Advantages
In structured cabling systems, MTP and MPO trunk cables provide an efficient way to route large fiber counts between distribution areas. A single trunk can replace numerous duplex runs, simplifying cable pathways and reducing congestion in trays and conduits.
This design improves manageability and scalability in backbone networks, where fiber counts are high and changes must be performed in an organized and repeatable way.
Flexibility Through Breakout Configurations
MTP and MPO cabling supports breakout configurations that convert a multi fiber connector into multiple duplex LC connections. This allows a single trunk to serve both parallel optical links and traditional duplex endpoints.
This flexibility is valuable in environments transitioning from duplex based designs to parallel optics, allowing existing infrastructure to be reused while supporting higher speed connections.
Signal Integrity And Optical Performance
High quality MTP and MPO assemblies are manufactured with precise fiber alignment and low insertion loss characteristics. Consistent performance across all fibers is essential for parallel optical systems, where imbalance can affect link stability.
Factory terminated MTP and MPO cables reduce variability compared to field terminated duplex assemblies, improving overall optical performance in dense deployments.
When Duplex Fiber Remains Appropriate
Duplex fiber remains suitable for lower speed links, longer distances, or environments where port density is not a concern. It is also often preferred for simple point to point connections or where frequent moves and changes involve single links rather than groups of fibers.
In these cases, the simplicity and flexibility of duplex fiber outweigh the density advantages of MTP and MPO cabling.
Typical Use Cases Favoring MTP And MPO
MTP and MPO cabling is commonly preferred in the following scenarios:
-
QSFP based 40 Gb and higher switch uplinks
-
Spine leaf and aggregation layer architectures
-
Data center backbone and inter row fiber trunks
-
High density patching environments with limited space
These use cases benefit from reduced cable count, improved organization, and scalable fiber management.
Best Practices For Deployment
Successful MTP and MPO deployment requires careful attention to polarity, connector cleanliness, and bend radius control. Polarity type must match transceiver requirements to ensure correct lane mapping.
Using pre tested, factory terminated assemblies and clearly labeled trunks helps reduce installation errors and simplifies future expansion.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
When should MTP or MPO be chosen over duplex fiber?
They should be chosen when high bandwidth, parallel optics, or high fiber density is required.
Are MTP and MPO cables only used for QSFP links?
No, they are also widely used for backbone trunks and structured fiber distribution.
Can MTP or MPO cabling be adapted to duplex connections?
Yes, breakout cables can convert multi fiber connectors into multiple duplex LC links.
Is polarity management required with MTP and MPO?
Yes, correct polarity is essential to ensure proper transmit and receive alignment.