What OCuLink 8x Cable Specifications Matter Most For PCIe 5.0 Performance?
Selecting an internal cable for PCIe 5.0 systems requires careful attention to electrical and mechanical specifications, not just connector compatibility. At Gen 5 signaling rates, small variations in impedance, loss, or routing discipline can determine whether a link trains reliably and sustains full bandwidth. Understanding which OCuLink 8x cable specifications matter most helps system builders avoid instability, retraining events, and hidden performance loss in high bandwidth platforms.
Lane Count And Native Link Width
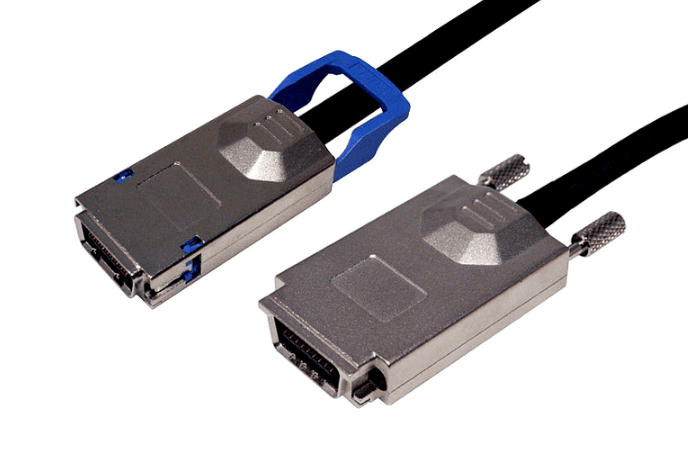
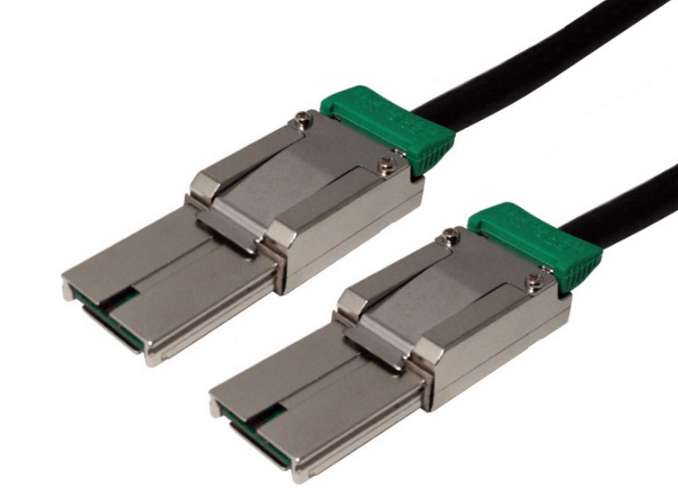
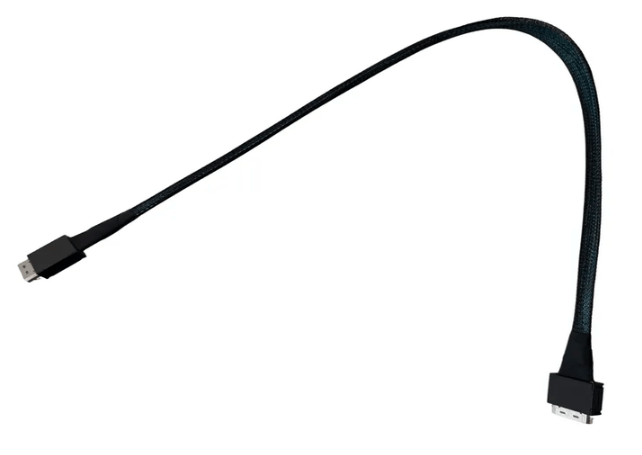
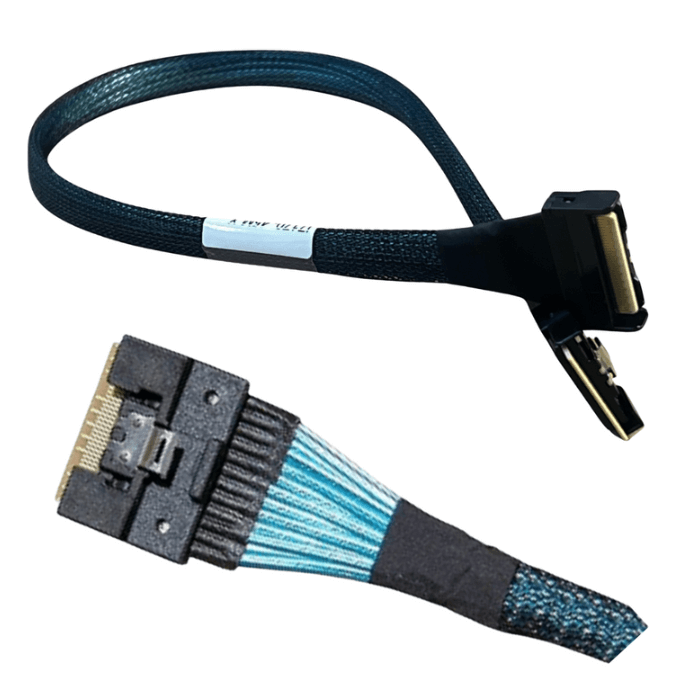
An OCuLink 8x cable is designed to carry eight PCIe lanes end to end, preserving a native x8 connection between host and device. This is essential for components such as GPUs, accelerators, and high performance NVMe backplanes that depend on sustained throughput.
Unlike breakout or bifurcated cables, an 8x to 8x OCuLink assembly does not split or remap lanes. Devices enumerate as a single x8 endpoint, which simplifies firmware behavior and reduces the risk of negotiation errors during link training.
Signal Integrity At PCIe 5.0 Speeds
PCIe 5.0 operates at twice the signaling rate of PCIe 4.0, leaving significantly less tolerance for electrical loss and noise. For OCuLink 8x cables, signal integrity specifications are the most critical factors influencing performance.
Key characteristics include controlled impedance across all differential pairs, low insertion loss over the supported cable length, and effective shielding to minimize crosstalk. These attributes help maintain clean eye openings and stable timing margins required for reliable Gen 5 operation.
Differential Pair Matching And Skew Control
With eight lanes operating in parallel, timing alignment across the cable is critical. Excessive skew between differential pairs can disrupt synchronization and force the link to retrain or downshift to a lower speed.
High quality OCuLink 8x cables are manufactured with precise conductor geometry and tightly matched pair lengths. This level of control ensures that all lanes arrive within PCIe 5.0 timing tolerances, even in dense chassis layouts with constrained routing paths.
Connector Quality And Mechanical Stability
OCuLink connectors are compact, but they must maintain precise alignment and consistent contact pressure to support high speed signaling. Secure latching mechanisms help prevent partial insertion or connector movement during service activity.
Mechanical instability can lead to intermittent errors that appear as CRC faults, performance drops, or unexpected device resets. Connector quality therefore has a direct impact on long term electrical reliability in PCIe 5.0 systems.
Cable Length And Routing Considerations
Cable length directly affects signal margin at Gen 5 speeds. Defined lengths such as 0.5 m and 1 m are commonly used to balance routing flexibility with electrical performance. Selecting the shortest practical length reduces insertion loss while allowing strain free routing.
Proper routing avoids tight bends and excessive tension that can alter conductor geometry over time. Clean routing also improves airflow and simplifies maintenance in compact servers and expansion chassis.
Backward Compatibility And Upgrade Flexibility
OCuLink 8x cables are backward compatible with earlier PCIe generations. When installed in PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 3.0 systems, the link negotiates down automatically while retaining the same mechanical and routing advantages.
This compatibility allows a single cable design to be used across mixed generation environments and supports future upgrades without reworking internal layouts.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What specification matters most for PCIe 5.0 OCuLink cabling?
Signal integrity factors such as impedance control, pair matching, and low insertion loss are the most important.
Does an OCuLink 8x cable add latency?
No. It provides a direct PCIe connection without retimers, switches, or additional protocol layers.
Are all OCuLink 8x cables suitable for PCIe 5.0?
No. Only cables specifically designed and validated for PCIe 5.0 should be used at Gen 5 speeds.
Can poor cabling cause PCIe links to downtrain?
Yes. Inadequate signal quality or improper routing can cause links to negotiate lower speeds or reduced widths.