The Differences Between SFF-8644 And SFF-8654 Connectors
SFF-8644 and SFF-8654 are both Small Form Factor connector standards used in enterprise storage and compute systems, but they are designed for very different roles. While they may appear similar in function, each standard targets a distinct deployment environment, signaling requirement, and mechanical use case. Understanding these differences is essential when selecting the correct connector for internal or external cabling in modern systems.
Intended Deployment Environment
The most fundamental difference between SFF-8644 and SFF-8654 is where they are designed to be used.
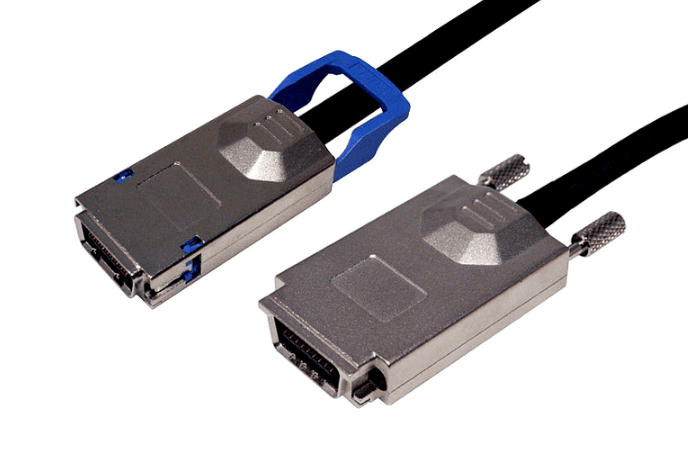
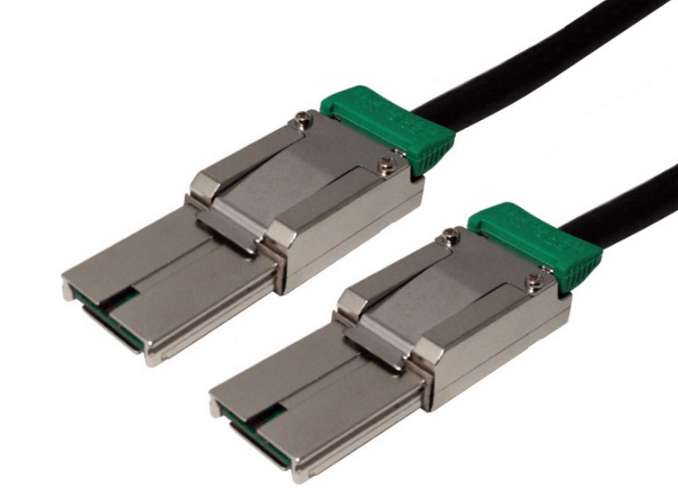
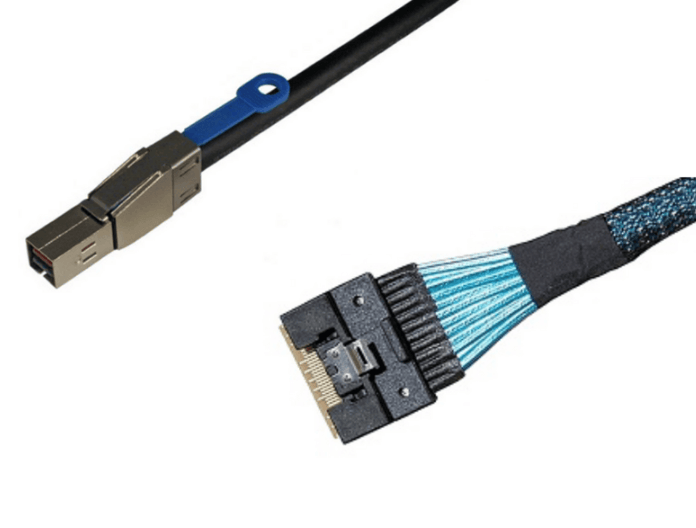
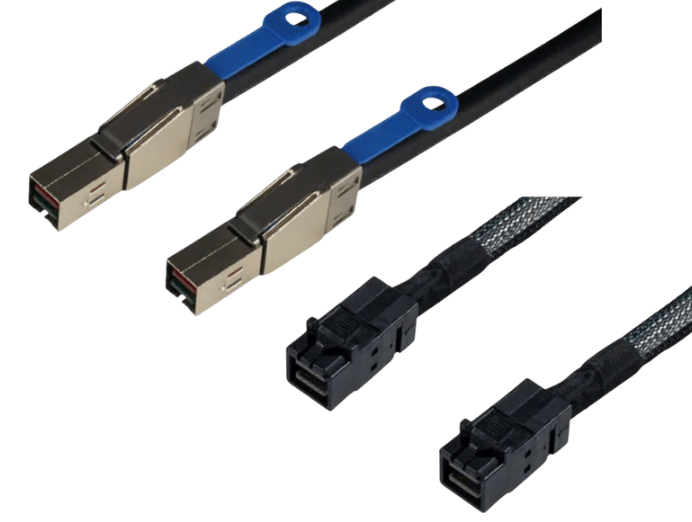
SFF-8644 defines the external HD MiniSAS connector. It is intended for connections that leave the server chassis, such as linking a host bus adapter to an external storage enclosure or JBOD. The connector and cable construction prioritize durability, shielding, and signal stability over longer external cable runs.
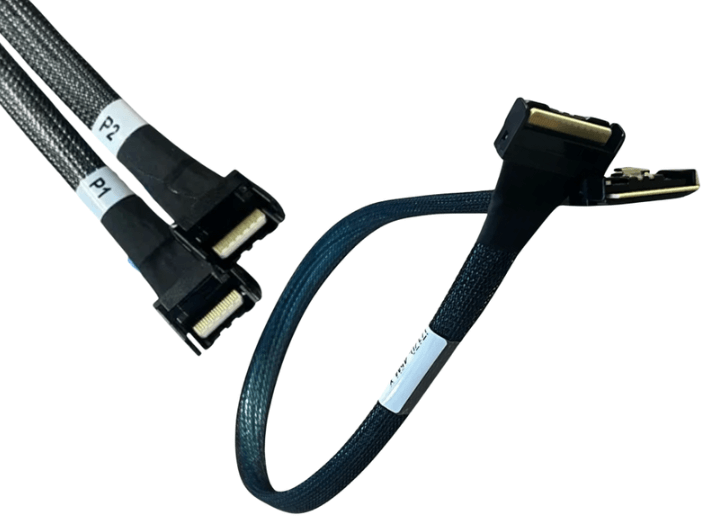
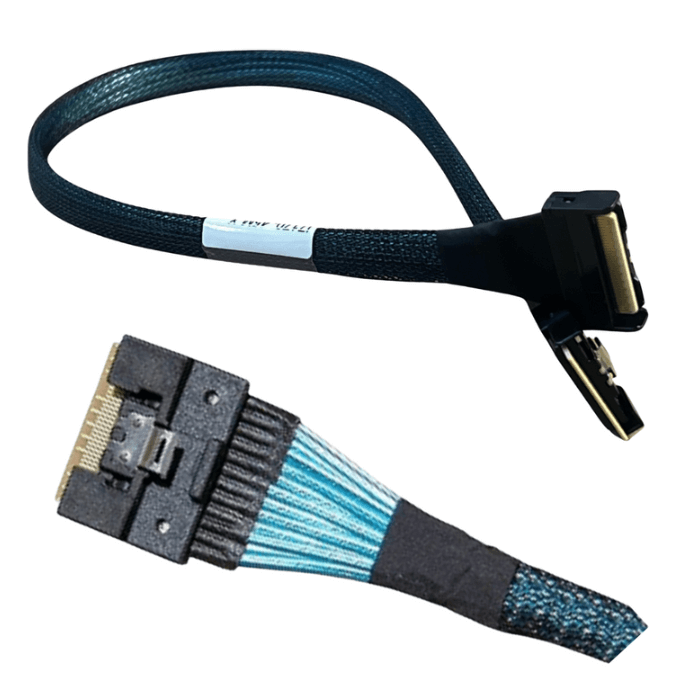
SFF-8654 defines the SlimSAS connector, which is designed exclusively for internal use. It connects controllers, backplanes, expanders, and drives inside a server or storage chassis where space is limited and cable runs are short.
Connector Size and Density
SFF-8654 is significantly smaller than SFF-8644. The SlimSAS design allows much higher port density on PCBs and backplanes, making it well suited for high density server architectures.
SFF-8644 has a larger mechanical footprint. This is acceptable in external environments where spacing is less constrained, but it limits how many ports can be placed on a single card or enclosure.
For dense internal layouts, SFF-8654 enables more connections in the same physical area.
Lane Configurations and Bandwidth
SFF-8644 typically supports four high speed lanes per connector. It is commonly used with SAS 2.0 and SAS 3.0 signaling, supporting data rates up to 12 Gb per second per lane.
SFF-8654 supports both 4 lane and 8 lane configurations, referred to as SlimSAS 4i and SlimSAS 8i. It is designed to support newer protocols, including SAS 4.0 at 24 Gb per second per lane and PCIe Gen 4 and newer signaling.
This makes SFF-8654 more scalable for modern high bandwidth internal designs.
Protocol Support Differences
SFF-8644 is primarily associated with SAS based storage expansion. While it can be used in some PCIe related designs, its ecosystem and typical usage are centered on external SAS connectivity.
SFF-8654 is protocol flexible. It can carry SAS, SATA, or PCIe signals depending on system design. This flexibility allows a single connector standard to support NVMe storage, SAS drives, or hybrid platforms.
This makes SFF-8654 particularly valuable in systems transitioning from SAS to PCIe based storage.
Cable Length and Signal Integrity Considerations
SFF-8644 cables are designed for longer runs compared to internal cabling. External cables feature heavier shielding and construction to protect against electromagnetic interference and physical handling.
SFF-8654 cables are optimized for short reach internal connections. Their electrical design focuses on maintaining signal integrity at very high data rates over shorter distances rather than long cable lengths.
Using an internal SlimSAS connector for external cabling or vice versa would violate design assumptions and can lead to signal or reliability issues.
Mechanical Robustness and Handling
External SFF-8644 connectors are designed to withstand repeated insertion cycles, cable strain, and rack level handling. They typically include stronger latching mechanisms and thicker cable jackets.
SFF-8654 connectors are optimized for internal assembly and service. They are compact and secure but not intended for frequent reconnection or exposure outside the chassis.
This distinction reflects their different operational environments.
Typical Use Cases
SFF-8644 is commonly used for:
-
Server to external storage enclosure connections
-
JBOD and expansion shelf links
-
External RAID and HBA connectivity
SFF-8654 is commonly used for:
-
Internal server backplanes
-
NVMe and SAS drive connections
-
PCIe switch and expander links
-
High density internal storage architectures
Each connector excels when used in its intended context.
Selection Guidance
Choose SFF-8644 when the connection must exit the chassis and maintain signal integrity over an external cable. It is the correct choice for storage expansion and rack level interconnects.
Choose SFF-8654 when designing internal systems that require high bandwidth, compact routing, and support for modern PCIe or SAS standards. It is optimized for dense layouts and next generation signaling.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are SFF-8644 and SFF-8654 interchangeable?
No. They are mechanically and electrically different and are not compatible.
Can SFF-8654 be used for external connections?
No. It is designed for internal use only and lacks the mechanical and shielding characteristics required for external cabling.
Which connector supports higher bandwidth?
SFF-8654 supports higher aggregate bandwidth due to 8 lane configurations and support for newer protocols.
Is SFF-8644 obsolete?
No. It remains widely used for external SAS storage connectivity.