The Difference Between Internal And External HD MiniSAS Cables
Internal and external HD MiniSAS cables serve very different roles, even though they share a similar name and support the same SAS generations. The key differences come down to connector type, physical construction, intended environment, and how the cable is expected to be handled. Confusing the two is a common and costly mistake in server and storage builds.
Connector Standards Define The Difference
The most important distinction is the connector specification.
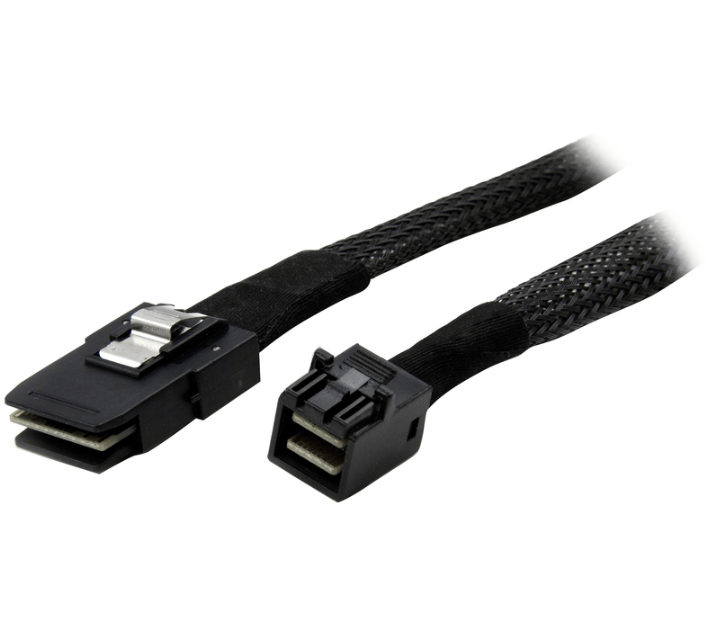
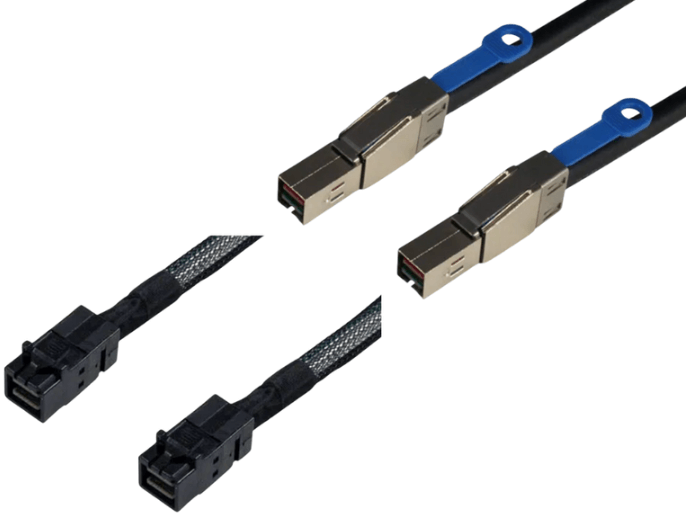
Internal HD MiniSAS uses the SFF-8643 connector. It is designed exclusively for use inside a chassis and mates with internal ports on RAID cards, HBAs, motherboards, and backplanes.
External HD MiniSAS uses the SFF-8644 connector. It is physically larger, fully enclosed in a metal shell, and designed to connect separate systems such as a server and an external storage enclosure.
These connectors are not mechanically compatible. An internal cable will not fit an external port, and an external cable will not fit an internal port.
Cable Construction and Durability
Internal HD MiniSAS cables are built for protected environments. They are typically shorter, lighter, and more flexible, optimized for routing inside a server where airflow is controlled and physical exposure is minimal. Shielding is sufficient for internal EMI levels but not intended for open rack or external routing.
External HD MiniSAS cables are far more rugged. They use thicker jackets, heavier shielding, reinforced strain relief, and secure latching mechanisms. This construction allows them to withstand vibration, EMI, and frequent insertion and removal in data center environments.
Intended Routing Environment
Internal HD MiniSAS cables must remain entirely inside the chassis. They connect components such as:
-
Controller card to backplane
-
Motherboard to drive cage
-
Internal SAS expanders
External HD MiniSAS cables are used when the connection leaves the chassis. Common examples include:
-
Server to JBOD
-
Server to external storage shelf
-
Rack to rack storage expansion
Using an internal cable outside the chassis exposes it to EMI and mechanical stress it was never designed to handle.
Performance and Protocol Support
From a protocol perspective, both internal and external HD MiniSAS cables support the same core standards.
They can carry SAS 2.0, SAS 3.0, and in many platforms SAS 4.0 signaling. Per lane speeds are dictated by the controller and backplane, not by whether the cable is internal or external.
The difference is not speed, but reliability over distance and environment. External cables are validated for longer runs and noisier conditions, while internal cables are optimized for short, controlled paths.
Length and Signal Integrity Considerations
Internal HD MiniSAS cables are intended for short distances within a chassis. Longer lengths increase attenuation and susceptibility to noise.
External HD MiniSAS cables are designed to maintain signal integrity over longer distances between systems. Their additional shielding and construction help preserve performance where internal cables would struggle.
Mechanical Handling and Service Life
Internal connectors are not meant for frequent reconnection. Once installed, they typically remain untouched until hardware service or replacement.
External connectors are designed for repeated mating cycles. They tolerate regular plugging and unplugging, which is common in expandable storage environments.
This difference matters in labs, data centers, and production environments where configurations change over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
A frequent mistake is assuming that “HD MiniSAS” refers to a single interchangeable cable type. The internal and external versions are fundamentally different.
Another common error is attempting to route an internal cable through a chassis opening to connect to an external enclosure. This often leads to EMI issues, intermittent errors, or physical cable failure.
Always verify the port type before selecting a cable.
How to Choose The Correct HD MiniSAS Cable
Choose internal HD MiniSAS (SFF-8643) when the entire connection stays inside a server or storage enclosure.
Choose external HD MiniSAS (SFF-8644) when connecting two separate systems or routing outside the chassis.
There is no safe or supported way to substitute one for the other.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are internal and external HD MiniSAS cables interchangeable?
No. They use different connectors and are designed for different environments.
Do both support the same SAS speeds?
Yes. Speed depends on the system, not whether the cable is internal or external.
Can an internal cable be used externally in an emergency?
No. It lacks the shielding and durability required for external use.
How can I quickly identify which one I need?
If the cable stays inside the chassis, use SFF-8643. If it connects to another enclosure, use SFF-8644.